|
Opens a form in order to initiate GPS position acquisition via a serial port or over a IP network using UDP.
Set the parameters to the required settings and click 'OK' to start using them.
(more information about GPS see 'How to > Use GPS data')
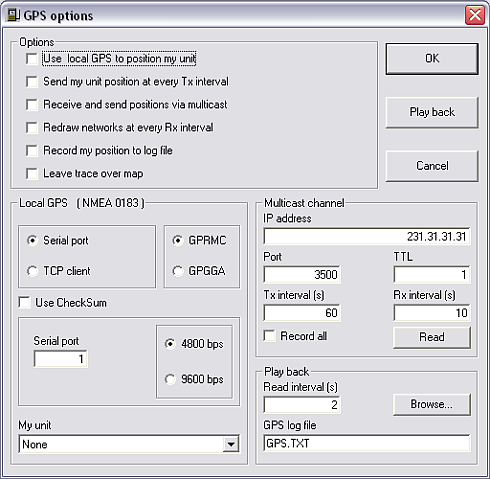
Options
Use local GPS to position my unit
Enables local GPS.
Send my unit position at every TX interval
Enables the broadcast of own position at the set interval.
Redraw networks at each RX interval
Enables redraw and calculation of all paths in a radionetwork.
Record my position to log-file
Enables logging of GPS data.
Leave trace over map
If checked a trace of the GPS positions is drawn on the map.
Local GPS (NMEA 1083)
Serial port, TCP client
Select the type of GPS source.
Serial is a direct serial connection to a GPS, TCP client is GPS distributed over a network.
GPRMC, GPGGA
Select the NMEA datagram. The program looks for a sentence beginning with $GPRMC from the GPS. This sentence is common to most GPS.
Serial port
Select the serial port of your PC that has the GPS receiver connected to.
Most GPS are capable of sending information through a simple serial link. Only the TXD and GROUND pins need to be connected to the PC, on any of the serial port.
4800 bps, 9600 bps
Select the bitrate. The GPS must be set at 4800 or 9600 bps, 8 bits, No Parity, and 1 stop bit.
Multicast channel
The program uses Multicast UDP protocol to report position to other PCs running the program. This protocol is common to most LAN and can be used on the Internet, as soon as the IP address (or domain name, or computer ID) and port are valid.
IP address
The destination address of the multicast
Port
IP-port
TTL
Time to live
TX interval (S)
Broadcast interval at which the GPS position form the serial port is broadcasted on the multicast channel.
RX interval (S)
Interval at which the received GPS position over the multicast channel is applied to the current network
Read
Immediate read of the multicast channel.
Playback
Read intervals
Interval at which the read GPS position of the file is applied to the current network
GPS logfile
Name of the logfile
Browse
Browse to the directory that holds the GPS file
Step by step
(more information about GPS see 'How to > Use GPS data')
- In Options menu select GPS options
- Enter the serial port at which the GPS is connected.
- Enter unit to move. This is the unit that will move according to the GPS position received.
- Enter IP address and port at which position will be reported.
- Press Start to initiate local GPS decoding. Color dot on the Status Bar should flash to show activity.
- If Log was checked, sentences will be saved on file. Use Play back to verify.
|